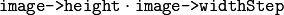Basic Structures¶
CvPoint¶
- CvPoint¶
2D point with integer coordinates (usually zero-based).
typedef struct CvPoint
{
int x;
int y;
}
CvPoint;
/* Constructor */
inline CvPoint cvPoint( int x, int y );
/* Conversion from CvPoint2D32f */
inline CvPoint cvPointFrom32f( CvPoint2D32f point );
CvPoint2D32f¶
- CvPoint2D32f¶
2D point with floating-point coordinates
typedef struct CvPoint2D32f
{
float x;
float y;
}
CvPoint2D32f;
- x
x-coordinate
- y
y-coordinate
/* Constructor */
inline CvPoint2D32f cvPoint2D32f( double x, double y );
/* Conversion from CvPoint */
inline CvPoint2D32f cvPointTo32f( CvPoint point );
CvPoint3D32f¶
- CvPoint3D32f¶
3D point with floating-point coordinates
typedef struct CvPoint3D32f
{
float x;
float y;
float z;
}
CvPoint3D32f;
/* Constructor */
inline CvPoint3D32f cvPoint3D32f( double x, double y, double z );
CvPoint2D64f¶
- CvPoint2D64f¶
2D point with double precision floating-point coordinates
typedef struct CvPoint2D64f
{
double x;
double y;
}
CvPoint2D64f;
- x
x-coordinate
- y
y-coordinate
/* Constructor */
inline CvPoint2D64f cvPoint2D64f( double x, double y );
/* Conversion from CvPoint */
inline CvPoint2D64f cvPointTo64f( CvPoint point );
CvPoint3D64f¶
- CvPoint3D64f¶
3D point with double precision floating-point coordinates
typedef struct CvPoint3D64f
{
double x;
double y;
double z;
}
CvPoint3D64f;
- x
x-coordinate
- y
y-coordinate
- z
z-coordinate
/* Constructor */
inline CvPoint3D64f cvPoint3D64f( double x, double y, double z );
CvSize¶
- CvSize¶
Pixel-accurate size of a rectangle.
typedef struct CvSize
{
int width;
int height;
}
CvSize;
/* Constructor */
inline CvSize cvSize( int width, int height );
CvSize2D32f¶
- CvSize2D32f¶
Sub-pixel accurate size of a rectangle.
typedef struct CvSize2D32f
{
float width;
float height;
}
CvSize2D32f;
- width
Width of the rectangle
- height
Height of the rectangle
/* Constructor */
inline CvSize2D32f cvSize2D32f( double width, double height );
CvRect¶
- CvRect¶
Offset (usually the top-left corner) and size of a rectangle.
typedef struct CvRect
{
int x;
int y;
int width;
int height;
}
CvRect;
- x
x-coordinate of the top-left corner
- y
y-coordinate of the top-left corner (bottom-left for Windows bitmaps)
- width
Width of the rectangle
- height
Height of the rectangle
/* Constructor */
inline CvRect cvRect( int x, int y, int width, int height );
CvScalar¶
- CvScalar¶
A container for 1-,2-,3- or 4-tuples of doubles.
typedef struct CvScalar
{
double val[4];
}
CvScalar;
/* Constructor:
initializes val[0] with val0, val[1] with val1, etc.
*/
inline CvScalar cvScalar( double val0, double val1=0,
double val2=0, double val3=0 );
/* Constructor:
initializes all of val[0]...val[3] with val0123
*/
inline CvScalar cvScalarAll( double val0123 );
/* Constructor:
initializes val[0] with val0, and all of val[1]...val[3] with zeros
*/
inline CvScalar cvRealScalar( double val0 );
CvTermCriteria¶
- CvTermCriteria¶
Termination criteria for iterative algorithms.
#define CV_TERMCRIT_ITER 1
#define CV_TERMCRIT_NUMBER CV_TERMCRIT_ITER
#define CV_TERMCRIT_EPS 2
typedef struct CvTermCriteria
{
int type;
int max_iter;
double epsilon;
}
CvTermCriteria;
/* Constructor */
inline CvTermCriteria cvTermCriteria( int type, int max_iter, double epsilon );
/* Check and transform a CvTermCriteria so that
type=CV_TERMCRIT_ITER+CV_TERMCRIT_EPS
and both max_iter and epsilon are valid */
CvTermCriteria cvCheckTermCriteria( CvTermCriteria criteria,
double default_eps,
int default_max_iters );
CvMat¶
- CvMat¶
A multi-channel matrix.
typedef struct CvMat
{
int type;
int step;
int* refcount;
union
{
uchar* ptr;
short* s;
int* i;
float* fl;
double* db;
} data;
#ifdef __cplusplus
union
{
int rows;
int height;
};
union
{
int cols;
int width;
};
#else
int rows;
int cols;
#endif
} CvMat;
Matrices are stored row by row. All of the rows are aligned by 4 bytes.
CvMatND¶
- CvMatND¶
Multi-dimensional dense multi-channel array.
typedef struct CvMatND
{
int type;
int dims;
int* refcount;
union
{
uchar* ptr;
short* s;
int* i;
float* fl;
double* db;
} data;
struct
{
int size;
int step;
}
dim[CV_MAX_DIM];
} CvMatND;
- type
A CvMatND signature (CV _ MATND _ MAGIC _ VAL), combining the type of elements and flags
- dims¶
The number of array dimensions
- refcount
Underlying data reference counter
- data
Pointers to the actual matrix data
- dim¶
For each dimension, the pair (number of elements, distance between elements in bytes)
CvSparseMat¶
- CvSparseMat¶
Multi-dimensional sparse multi-channel array.
typedef struct CvSparseMat
{
int type;
int dims;
int* refcount;
struct CvSet* heap;
void** hashtable;
int hashsize;
int total;
int valoffset;
int idxoffset;
int size[CV_MAX_DIM];
} CvSparseMat;
- type
A CvSparseMat signature (CV _ SPARSE _ MAT _ MAGIC _ VAL), combining the type of elements and flags.
- dims
Number of dimensions
- refcount
Underlying reference counter. Not used.
- heap¶
A pool of hash table nodes
- hashtable¶
The hash table. Each entry is a list of nodes.
- hashsize¶
Size of the hash table
- total¶
Total number of sparse array nodes
- valoffset¶
The value offset of the array nodes, in bytes
- idxoffset¶
The index offset of the array nodes, in bytes
- size¶
Array of dimension sizes
IplImage¶
- IplImage¶
IPL image header
typedef struct _IplImage
{
int nSize;
int ID;
int nChannels;
int alphaChannel;
int depth;
char colorModel[4];
char channelSeq[4];
int dataOrder;
int origin;
int align;
int width;
int height;
struct _IplROI *roi;
struct _IplImage *maskROI;
void *imageId;
struct _IplTileInfo *tileInfo;
int imageSize;
char *imageData;
int widthStep;
int BorderMode[4];
int BorderConst[4];
char *imageDataOrigin;
}
IplImage;
- nSize¶
sizeof(IplImage)
- ID¶
Version, always equals 0
- nChannels¶
Number of channels. Most OpenCV functions support 1-4 channels.
- alphaChannel¶
Ignored by OpenCV
- depth¶
Channel depth in bits + the optional sign bit ( IPL_DEPTH_SIGN ). The supported depths are:
- colorModel¶
Ignored by OpenCV. The OpenCV function CvtColor requires the source and destination color spaces as parameters.
- channelSeq¶
Ignored by OpenCV
- dataOrder¶
0 = IPL_DATA_ORDER_PIXEL - interleaved color channels, 1 - separate color channels. CreateImage only creates images with interleaved channels. For example, the usual layout of a color image is:
- origin¶
0 - top-left origin, 1 - bottom-left origin (Windows bitmap style)
- align¶
Alignment of image rows (4 or 8). OpenCV ignores this and uses widthStep instead.
- width
Image width in pixels
- height
Image height in pixels
- roi¶
Region Of Interest (ROI). If not NULL, only this image region will be processed.
- maskROI¶
Must be NULL in OpenCV
- imageId¶
Must be NULL in OpenCV
- tileInfo¶
Must be NULL in OpenCV
- imageSize¶
Image data size in bytes. For interleaved data, this equals
- imageData¶
A pointer to the aligned image data
- widthStep¶
The size of an aligned image row, in bytes
- BorderMode¶
Border completion mode, ignored by OpenCV
- BorderConst¶
Border completion mode, ignored by OpenCV
- imageDataOrigin¶
A pointer to the origin of the image data (not necessarily aligned). This is used for image deallocation.
The IplImage structure was inherited from the Intel Image Processing Library, in which the format is native. OpenCV only supports a subset of possible IplImage formats, as outlined in the parameter list above.
In addition to the above restrictions, OpenCV handles ROIs differently. OpenCV functions require that the image size or ROI size of all source and destination images match exactly. On the other hand, the Intel Image Processing Library processes the area of intersection between the source and destination images (or ROIs), allowing them to vary independently.
CvArr¶
- CvArr¶
Arbitrary array
typedef void CvArr;
The metatype CvArr is used only as a function parameter to specify that the function accepts arrays of multiple types, such as IplImage*, CvMat* or even CvSeq* sometimes. The particular array type is determined at runtime by analyzing the first 4 bytes of the header.
Help and Feedback
You did not find what you were looking for?- Ask a question in the user group/mailing list.
- If you think something is missing or wrong in the documentation, please file a bug report.