Feature Detection¶
Canny¶
- Canny(image, edges, threshold1, threshold2, aperture_size=3) → None¶
Implements the Canny algorithm for edge detection.
Parameters:
The function finds the edges on the input image image and marks them in the output image edges using the Canny algorithm. The smallest value between threshold1 and threshold2 is used for edge linking, the largest value is used to find the initial segments of strong edges.
CornerEigenValsAndVecs¶
- CornerEigenValsAndVecs(image, eigenvv, blockSize, aperture_size=3) → None¶
Calculates eigenvalues and eigenvectors of image blocks for corner detection.
Parameters:
For every pixel, the function
cvCornerEigenValsAndVecs
considers a
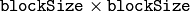 neigborhood S(p). It calcualtes the covariation matrix of derivatives over the neigborhood as:
neigborhood S(p). It calcualtes the covariation matrix of derivatives over the neigborhood as:
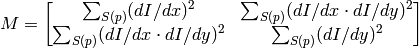
After that it finds eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the matrix and stores them into destination image in form
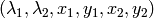 where
where
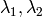
are the eigenvalues of
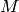 ; not sorted
; not sorted
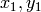
are the eigenvectors corresponding to
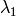
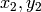
are the eigenvectors corresponding to
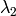
CornerHarris¶
- CornerHarris(image, harris_dst, blockSize, aperture_size=3, k=0.04) → None¶
Harris edge detector.
Parameters: - image (CvArr) – Input image
- harris_dst (CvArr) – Image to store the Harris detector responses. Should have the same size as image
- blockSize (int) – Neighborhood size (see the discussion of CornerEigenValsAndVecs )
- aperture_size (int) – Aperture parameter for the Sobel operator (see Sobel ).
- k (float) – Harris detector free parameter. See the formula below
The function runs the Harris edge detector on the image. Similarly to
CornerMinEigenVal
and
CornerEigenValsAndVecs
, for each pixel it calculates a
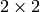 gradient covariation matrix
gradient covariation matrix
 over a
over a
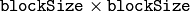 neighborhood. Then, it stores
neighborhood. Then, it stores
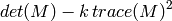
to the destination image. Corners in the image can be found as the local maxima of the destination image.
CornerMinEigenVal¶
- CornerMinEigenVal(image, eigenval, blockSize, aperture_size=3) → None¶
Calculates the minimal eigenvalue of gradient matrices for corner detection.
Parameters: - image (CvArr) – Input image
- eigenval (CvArr) – Image to store the minimal eigenvalues. Should have the same size as image
- blockSize (int) – Neighborhood size (see the discussion of CornerEigenValsAndVecs )
- aperture_size (int) – Aperture parameter for the Sobel operator (see Sobel ).
The function is similar to
CornerEigenValsAndVecs
but it calculates and stores only the minimal eigen value of derivative covariation matrix for every pixel, i.e.
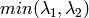 in terms of the previous function.
in terms of the previous function.
FindCornerSubPix¶
- FindCornerSubPix(image, corners, win, zero_zone, criteria) → corners¶
Refines the corner locations.
Parameters: - image (CvArr) – Input image
- corners (sequence of (float, float)) – Initial coordinates of the input corners as a list of (x, y) pairs
- win (CvSize) – Half of the side length of the search window. For example, if win =(5,5), then a
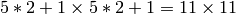 search window would be used
search window would be used - zero_zone (CvSize) – Half of the size of the dead region in the middle of the search zone over which the summation in the formula below is not done. It is used sometimes to avoid possible singularities of the autocorrelation matrix. The value of (-1,-1) indicates that there is no such size
- criteria (CvTermCriteria) – Criteria for termination of the iterative process of corner refinement. That is, the process of corner position refinement stops either after a certain number of iterations or when a required accuracy is achieved. The criteria may specify either of or both the maximum number of iteration and the required accuracy
The function iterates to find the sub-pixel accurate location of corners, or radial saddle points, as shown in on the picture below. It returns the refined coordinates as a list of (x, y) pairs.
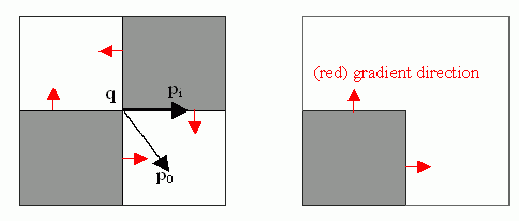
Sub-pixel accurate corner locator is based on the observation that every vector from the center
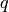 to a point
to a point
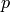 located within a neighborhood of
located within a neighborhood of
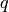 is orthogonal to the image gradient at
is orthogonal to the image gradient at
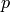 subject to image and measurement noise. Consider the expression:
subject to image and measurement noise. Consider the expression:
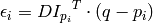
where
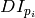 is the image gradient at the one of the points
is the image gradient at the one of the points
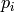 in a neighborhood of
in a neighborhood of
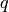 . The value of
. The value of
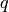 is to be found such that
is to be found such that
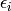 is minimized. A system of equations may be set up with
is minimized. A system of equations may be set up with
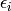 set to zero:
set to zero:
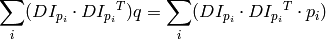
where the gradients are summed within a neighborhood (“search window”) of
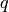 . Calling the first gradient term
. Calling the first gradient term
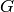 and the second gradient term
and the second gradient term
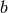 gives:
gives:
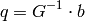
The algorithm sets the center of the neighborhood window at this new center
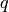 and then iterates until the center keeps within a set threshold.
and then iterates until the center keeps within a set threshold.
GoodFeaturesToTrack¶
- GoodFeaturesToTrack(image, eigImage, tempImage, cornerCount, qualityLevel, minDistance, mask=NULL, blockSize=3, useHarris=0, k=0.04) → corners¶
Determines strong corners on an image.
Parameters: - image (CvArr) – The source 8-bit or floating-point 32-bit, single-channel image
- eigImage (CvArr) – Temporary floating-point 32-bit image, the same size as image
- tempImage (CvArr) – Another temporary image, the same size and format as eigImage
- cornerCount (int) – number of corners to detect
- qualityLevel (float) – Multiplier for the max/min eigenvalue; specifies the minimal accepted quality of image corners
- minDistance (float) – Limit, specifying the minimum possible distance between the returned corners; Euclidian distance is used
- mask (CvArr) – Region of interest. The function selects points either in the specified region or in the whole image if the mask is NULL
- blockSize (int) – Size of the averaging block, passed to the underlying CornerMinEigenVal or CornerHarris used by the function
- useHarris (int) – If nonzero, Harris operator ( CornerHarris ) is used instead of default CornerMinEigenVal
- k (float) – Free parameter of Harris detector; used only if (
 )
)
The function finds the corners with big eigenvalues in the image. The function first calculates the minimal
eigenvalue for every source image pixel using the
CornerMinEigenVal
function and stores them in
eigImage
. Then it performs
non-maxima suppression (only the local maxima in
 neighborhood
are retained). The next step rejects the corners with the minimal
eigenvalue less than
neighborhood
are retained). The next step rejects the corners with the minimal
eigenvalue less than
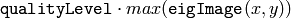 .
Finally, the function ensures that the distance between any two corners is not smaller than
minDistance
. The weaker corners (with a smaller min eigenvalue) that are too close to the stronger corners are rejected.
.
Finally, the function ensures that the distance between any two corners is not smaller than
minDistance
. The weaker corners (with a smaller min eigenvalue) that are too close to the stronger corners are rejected.
Note that the if the function is called with different values A and B of the parameter qualityLevel , and A > {B}, the array of returned corners with qualityLevel=A will be the prefix of the output corners array with qualityLevel=B .
HoughLines2¶
- HoughLines2(image, storage, method, rho, theta, threshold, param1=0, param2=0) → lines¶
Finds lines in a binary image using a Hough transform.
Parameters: - image (CvArr) – The 8-bit, single-channel, binary source image. In the case of a probabilistic method, the image is modified by the function
- storage (CvMemStorage) – The storage for the lines that are detected. It can be a memory storage (in this case a sequence of lines is created in the storage and returned by the function) or single row/single column matrix (CvMat*) of a particular type (see below) to which the lines’ parameters are written. The matrix header is modified by the function so its cols or rows will contain the number of lines detected. If storage is a matrix and the actual number of lines exceeds the matrix size, the maximum possible number of lines is returned (in the case of standard hough transform the lines are sorted by the accumulator value)
- method (int) –
The Hough transform variant, one of the following:
- CV_HOUGH_STANDARD classical or standard Hough transform. Every line is represented by two floating-point numbers
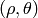 , where
, where 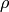 is a distance between (0,0) point and the line, and
is a distance between (0,0) point and the line, and 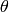 is the angle between x-axis and the normal to the line. Thus, the matrix must be (the created sequence will be) of CV_32FC2 type
is the angle between x-axis and the normal to the line. Thus, the matrix must be (the created sequence will be) of CV_32FC2 type - CV_HOUGH_PROBABILISTIC probabilistic Hough transform (more efficient in case if picture contains a few long linear segments). It returns line segments rather than the whole line. Each segment is represented by starting and ending points, and the matrix must be (the created sequence will be) of CV_32SC4 type
- CV_HOUGH_MULTI_SCALE multi-scale variant of the classical Hough transform. The lines are encoded the same way as CV_HOUGH_STANDARD
- CV_HOUGH_STANDARD classical or standard Hough transform. Every line is represented by two floating-point numbers
- rho (float) – Distance resolution in pixel-related units
- theta (float) – Angle resolution measured in radians
- threshold (int) – Threshold parameter. A line is returned by the function if the corresponding accumulator value is greater than threshold
- param1 (float) –
The first method-dependent parameter:
- For the classical Hough transform it is not used (0).
- For the probabilistic Hough transform it is the minimum line length.
- For the multi-scale Hough transform it is the divisor for the distance resolution
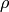 . (The coarse distance resolution will be
. (The coarse distance resolution will be 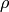 and the accurate resolution will be
and the accurate resolution will be 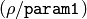 ).
).
- param2 (float) –
The second method-dependent parameter:
- For the classical Hough transform it is not used (0).
- For the probabilistic Hough transform it is the maximum gap between line segments lying on the same line to treat them as a single line segment (i.e. to join them).
- For the multi-scale Hough transform it is the divisor for the angle resolution
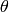 . (The coarse angle resolution will be
. (The coarse angle resolution will be 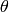 and the accurate resolution will be
and the accurate resolution will be 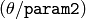 ).
).
The function implements a few variants of the Hough transform for line detection.
PreCornerDetect¶
- PreCornerDetect(image, corners, apertureSize=3) → None¶
Calculates the feature map for corner detection.
Parameters:
The function calculates the function
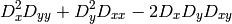
where
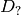 denotes one of the first image derivatives and
denotes one of the first image derivatives and
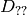 denotes a second image derivative.
denotes a second image derivative.
The corners can be found as local maximums of the function below:
Help and Feedback
You did not find what you were looking for?- Try the Cookbook.
- Ask a question in the user group/mailing list.
- If you think something is missing or wrong in the documentation, please file a bug report.
