Drawing Functions¶
Drawing functions work with matrices/images of arbitrary depth. The boundaries of the shapes can be rendered with antialiasing (implemented only for 8-bit images for now). All the functions include the parameter color that uses a rgb value (that may be constructed with CV_RGB ) for color images and brightness for grayscale images. For color images the order channel is normally Blue, Green, Red , this is what imshow() , imread() and imwrite() expect If you are using your own image rendering and I/O functions, you can use any channel ordering, the drawing functions process each channel independently and do not depend on the channel order or even on the color space used. The whole image can be converted from BGR to RGB or to a different color space using cvtColor() .
If a drawn figure is partially or completely outside the image, the drawing functions clip it. Also, many drawing functions can handle pixel coordinates specified with sub-pixel accuracy, that is, the coordinates can be passed as fixed-point numbers, encoded as integers. The number of fractional bits is specified by the
shift
parameter and the real point coordinates are calculated as
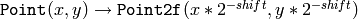 . This feature is especially effective wehn rendering antialiased shapes.
. This feature is especially effective wehn rendering antialiased shapes.
Also, note that the functions do not support alpha-transparency - when the target image is 4-channnel, then the color[3] is simply copied to the repainted pixels. Thus, if you want to paint semi-transparent shapes, you can paint them in a separate buffer and then blend it with the main image.
Circle¶
- Circle(img, center, radius, color, thickness=1, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Draws a circle.
Parameters: - img (CvArr) – Image where the circle is drawn
- center (CvPoint) – Center of the circle
- radius (int) – Radius of the circle
- color (CvScalar) – Circle color
- thickness (int) – Thickness of the circle outline if positive, otherwise this indicates that a filled circle is to be drawn
- lineType (int) – Type of the circle boundary, see Line description
- shift (int) – Number of fractional bits in the center coordinates and radius value
The function draws a simple or filled circle with a given center and radius.
ClipLine¶
- ClipLine(imgSize, pt1, pt2) -> (clipped_pt1, clipped_pt2)¶
Clips the line against the image rectangle.
Parameters:
The function calculates a part of the line segment which is entirely within the image. If the line segment is outside the image, it returns None. If the line segment is inside the image it returns a new pair of points.
DrawContours¶
- DrawContours(img, contour, external_color, hole_color, max_level, thickness=1, lineType=8, offset=(0, 0)) → None¶
Draws contour outlines or interiors in an image.
Parameters: - img (CvArr) – Image where the contours are to be drawn. As with any other drawing function, the contours are clipped with the ROI.
- contour (CvSeq) – Pointer to the first contour
- external_color (CvScalar) – Color of the external contours
- hole_color (CvScalar) – Color of internal contours (holes)
- max_level (int) – Maximal level for drawn contours. If 0, only contour is drawn. If 1, the contour and all contours following
it on the same level are drawn. If 2, all contours following and all
contours one level below the contours are drawn, and so forth. If the value
is negative, the function does not draw the contours following after contour but draws the child contours of contour up
to the
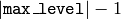 level.
level. - thickness (int) – Thickness of lines the contours are drawn with. If it is negative (For example, =CV _ FILLED), the contour interiors are drawn.
- lineType (int) – Type of the contour segments, see Line description
The function draws contour outlines in the image if
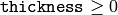 or fills the area bounded by the contours if
or fills the area bounded by the contours if
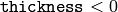 .
.
Ellipse¶
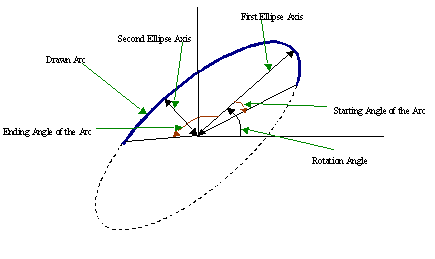
- Ellipse(img, center, axes, angle, start_angle, end_angle, color, thickness=1, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Draws a simple or thick elliptic arc or an fills ellipse sector.
Parameters: - img (CvArr) – The image
- center (CvPoint) – Center of the ellipse
- axes (CvSize) – Length of the ellipse axes
- angle (float) – Rotation angle
- start_angle (float) – Starting angle of the elliptic arc
- end_angle (float) – Ending angle of the elliptic arc.
- color (CvScalar) – Ellipse color
- thickness (int) – Thickness of the ellipse arc outline if positive, otherwise this indicates that a filled ellipse sector is to be drawn
- lineType (int) – Type of the ellipse boundary, see Line description
- shift (int) – Number of fractional bits in the center coordinates and axes’ values
The function draws a simple or thick elliptic arc or fills an ellipse sector. The arc is clipped by the ROI rectangle. A piecewise-linear approximation is used for antialiased arcs and thick arcs. All the angles are given in degrees. The picture below explains the meaning of the parameters.
Parameters of Elliptic Arc
EllipseBox¶
- EllipseBox(img, box, color, thickness=1, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Draws a simple or thick elliptic arc or fills an ellipse sector.
Parameters:
The function draws a simple or thick ellipse outline, or fills an ellipse. The functions provides a convenient way to draw an ellipse approximating some shape; that is what CamShift and FitEllipse do. The ellipse drawn is clipped by ROI rectangle. A piecewise-linear approximation is used for antialiased arcs and thick arcs.
FillConvexPoly¶
- FillConvexPoly(img, pn, color, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Fills a convex polygon.
Parameters:
The function fills a convex polygon’s interior. This function is much faster than the function cvFillPoly and can fill not only convex polygons but any monotonic polygon, i.e., a polygon whose contour intersects every horizontal line (scan line) twice at the most.
FillPoly¶
- FillPoly(img, polys, color, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Fills a polygon’s interior.
Parameters:
The function fills an area bounded by several polygonal contours. The function fills complex areas, for example, areas with holes, contour self-intersection, and so forth.
GetTextSize¶
- GetTextSize(textString, font)-> (textSize, baseline)¶
Retrieves the width and height of a text string.
Parameters: - font (CvFont) – Pointer to the font structure
- textString (str) – Input string
- textSize (CvSize) – Resultant size of the text string. Height of the text does not include the height of character parts that are below the baseline.
- baseline (int) – y-coordinate of the baseline relative to the bottom-most text point
The function calculates the dimensions of a rectangle to enclose a text string when a specified font is used.
InitFont¶
- InitFont(fontFace, hscale, vscale, shear=0, thickness=1, lineType=8) → font¶
Initializes font structure.
Parameters: - font (CvFont) – Pointer to the font structure initialized by the function
- fontFace (int) –
Font name identifier. Only a subset of Hershey fonts http://sources.isc.org/utils/misc/hershey-font.txt are supported now:
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX normal size sans-serif font
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN small size sans-serif font
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX normal size sans-serif font (more complex than CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX )
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX normal size serif font
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX normal size serif font (more complex than CV_FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX )
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL smaller version of CV_FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_SIMPLEX hand-writing style font
- CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX more complex variant of CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_SIMPLEX
The parameter can be composited from one of the values above and an optional CV_FONT_ITALIC flag, which indicates italic or oblique font.
- hscale (float) – Horizontal scale. If equal to 1.0f , the characters have the original width depending on the font type. If equal to 0.5f , the characters are of half the original width.
- vscale (float) – Vertical scale. If equal to 1.0f , the characters have the original height depending on the font type. If equal to 0.5f , the characters are of half the original height.
- shear (float) – Approximate tangent of the character slope relative to the vertical line. A zero value means a non-italic font, 1.0f means about a 45 degree slope, etc.
- thickness (int) – Thickness of the text strokes
- lineType (int) – Type of the strokes, see Line description
The function initializes the font structure that can be passed to text rendering functions.
InitLineIterator¶
- InitLineIterator(image, pt1, pt2, connectivity=8, left_to_right=0) → line_iterator¶
Initializes the line iterator.
Parameters: - image (CvArr) – Image to sample the line from
- pt1 (CvPoint) – First ending point of the line segment
- pt2 (CvPoint) – Second ending point of the line segment
- connectivity (int) – The scanned line connectivity, 4 or 8.
- left_to_right (int) – If (
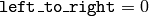 ) then the line is scanned in the specified order, from pt1 to pt2 .
If (
) then the line is scanned in the specified order, from pt1 to pt2 .
If ( 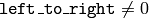 ) the line is scanned from left-most point to right-most.
) the line is scanned from left-most point to right-most. - line_iterator (iter) – Iterator over the pixels of the line
The function returns an iterator over the pixels connecting the two points. The points on the line are calculated one by one using a 4-connected or 8-connected Bresenham algorithm.
Example: Using line iterator to calculate the sum of pixel values along a color line
>>> import cv
>>> img = cv.LoadImageM("building.jpg", cv.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR)
>>> li = cv.InitLineIterator(img, (100, 100), (125, 150))
>>> red_sum = 0
>>> green_sum = 0
>>> blue_sum = 0
>>> for (r, g, b) in li:
... red_sum += r
... green_sum += g
... blue_sum += b
>>> print red_sum, green_sum, blue_sum
10935.0 9496.0 7946.0
or more concisely using zip :
>>> import cv
>>> img = cv.LoadImageM("building.jpg", cv.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR)
>>> li = cv.InitLineIterator(img, (100, 100), (125, 150))
>>> print [sum(c) for c in zip(*li)]
[10935.0, 9496.0, 7946.0]
Line¶
- Line(img, pt1, pt2, color, thickness=1, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Draws a line segment connecting two points.
Parameters: - img (CvArr) – The image
- pt1 (CvPoint) – First point of the line segment
- pt2 (CvPoint) – Second point of the line segment
- color (CvScalar) – Line color
- thickness (int) – Line thickness
- lineType (int) –
Type of the line:
- 8 (or omitted) 8-connected line.
- 4 4-connected line.
- CV_AA antialiased line.
- shift (int) – Number of fractional bits in the point coordinates
The function draws the line segment between pt1 and pt2 points in the image. The line is clipped by the image or ROI rectangle. For non-antialiased lines with integer coordinates the 8-connected or 4-connected Bresenham algorithm is used. Thick lines are drawn with rounding endings. Antialiased lines are drawn using Gaussian filtering. To specify the line color, the user may use the macro CV_RGB( r, g, b ) .
PolyLine¶
- PolyLine(img, polys, is_closed, color, thickness=1, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Draws simple or thick polygons.
Parameters: - polys (list of lists of (x,y) pairs) – List of lists of (x,y) pairs. Each list of points is a polygon.
- img (CvArr) – Image
- is_closed (int) – Indicates whether the polylines must be drawn closed. If closed, the function draws the line from the last vertex of every contour to the first vertex.
- color (CvScalar) – Polyline color
- thickness (int) – Thickness of the polyline edges
- lineType (int) – Type of the line segments, see Line description
- shift (int) – Number of fractional bits in the vertex coordinates
The function draws single or multiple polygonal curves.
PutText¶
- PutText(img, text, org, font, color) → None¶
Draws a text string.
Parameters:
The function renders the text in the image with the specified font and color. The printed text is clipped by the ROI rectangle. Symbols that do not belong to the specified font are replaced with the symbol for a rectangle.
Rectangle¶
- Rectangle(img, pt1, pt2, color, thickness=1, lineType=8, shift=0) → None¶
Draws a simple, thick, or filled rectangle.
Parameters: - img (CvArr) – Image
- pt1 (CvPoint) – One of the rectangle’s vertices
- pt2 (CvPoint) – Opposite rectangle vertex
- color (CvScalar) – Line color (RGB) or brightness (grayscale image)
- thickness (int) – Thickness of lines that make up the rectangle. Negative values, e.g., CV _ FILLED, cause the function to draw a filled rectangle.
- lineType (int) – Type of the line, see Line description
- shift (int) – Number of fractional bits in the point coordinates
The function draws a rectangle with two opposite corners pt1 and pt2 .
Help and Feedback
You did not find what you were looking for?- Try the FAQ.
- Ask a question in the user group/mailing list.
- If you think something is missing or wrong in the documentation, please file a bug report.
