Clustering¶
KMeans2¶
- int cvKMeans2(const CvArr* samples, int nclusters, CvArr* labels, CvTermCriteria termcrit, int attempts=1, CvRNG* rng=0, int flags=0, CvArr* centers=0, double* compactness=0)¶
Splits set of vectors by a given number of clusters.
Parameters: - samples – Floating-point matrix of input samples, one row per sample
- nclusters – Number of clusters to split the set by
- labels – Output integer vector storing cluster indices for every sample
- termcrit – Specifies maximum number of iterations and/or accuracy (distance the centers can move by between subsequent iterations)
- attempts – How many times the algorithm is executed using different initial labelings. The algorithm returns labels that yield the best compactness (see the last function parameter)
- rng – Optional external random number generator; can be used to fully control the function behaviour
- flags – Can be 0 or CV_KMEANS_USE_INITIAL_LABELS . The latter value means that during the first (and possibly the only) attempt, the function uses the user-supplied labels as the initial approximation instead of generating random labels. For the second and further attempts, the function will use randomly generated labels in any case
- centers – The optional output array of the cluster centers
- compactness – The optional output parameter, which is computed as
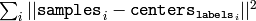 after every attempt; the best (minimum) value is chosen and the
corresponding labels are returned by the function. Basically, the
user can use only the core of the function, set the number of
attempts to 1, initialize labels each time using a custom algorithm
( flags=CV_KMEAN_USE_INITIAL_LABELS ) and, based on the output compactness
or any other criteria, choose the best clustering.
after every attempt; the best (minimum) value is chosen and the
corresponding labels are returned by the function. Basically, the
user can use only the core of the function, set the number of
attempts to 1, initialize labels each time using a custom algorithm
( flags=CV_KMEAN_USE_INITIAL_LABELS ) and, based on the output compactness
or any other criteria, choose the best clustering.
The function
cvKMeans2
implements a k-means algorithm that finds the
centers of
nclusters
clusters and groups the input samples
around the clusters. On output,
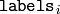 contains a cluster index for
samples stored in the i-th row of the
samples
matrix.
contains a cluster index for
samples stored in the i-th row of the
samples
matrix.
#include "cxcore.h"
#include "highgui.h"
void main( int argc, char** argv )
{
#define MAX_CLUSTERS 5
CvScalar color_tab[MAX_CLUSTERS];
IplImage* img = cvCreateImage( cvSize( 500, 500 ), 8, 3 );
CvRNG rng = cvRNG(0xffffffff);
color_tab[0] = CV_RGB(255,0,0);
color_tab[1] = CV_RGB(0,255,0);
color_tab[2] = CV_RGB(100,100,255);
color_tab[3] = CV_RGB(255,0,255);
color_tab[4] = CV_RGB(255,255,0);
cvNamedWindow( "clusters", 1 );
for(;;)
{
int k, cluster_count = cvRandInt(&rng)
int i, sample_count = cvRandInt(&rng)
CvMat* points = cvCreateMat( sample_count, 1, CV_32FC2 );
CvMat* clusters = cvCreateMat( sample_count, 1, CV_32SC1 );
/* generate random sample from multigaussian distribution */
for( k = 0; k < cluster_count; k++ )
{
CvPoint center;
CvMat point_chunk;
center.x = cvRandInt(&rng)
center.y = cvRandInt(&rng)
cvGetRows( points,
&point_chunk,
k*sample_count/cluster_count,
(k == (cluster_count - 1)) ?
sample_count :
(k+1)*sample_count/cluster_count );
cvRandArr( &rng, &point_chunk, CV_RAND_NORMAL,
cvScalar(center.x,center.y,0,0),
cvScalar(img->width/6, img->height/6,0,0) );
}
/* shuffle samples */
for( i = 0; i < sample_count/2; i++ )
{
CvPoint2D32f* pt1 =
(CvPoint2D32f*)points->data.fl + cvRandInt(&rng)
CvPoint2D32f* pt2 =
(CvPoint2D32f*)points->data.fl + cvRandInt(&rng)
CvPoint2D32f temp;
CV_SWAP( *pt1, *pt2, temp );
}
cvKMeans2( points, cluster_count, clusters,
cvTermCriteria( CV_TERMCRIT_EPS+CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 10, 1.0 ));
cvZero( img );
for( i = 0; i < sample_count; i++ )
{
CvPoint2D32f pt = ((CvPoint2D32f*)points->data.fl)[i];
int cluster_idx = clusters->data.i[i];
cvCircle( img,
cvPointFrom32f(pt),
2,
color_tab[cluster_idx],
CV_FILLED );
}
cvReleaseMat( &points );
cvReleaseMat( &clusters );
cvShowImage( "clusters", img );
int key = cvWaitKey(0);
if( key == 27 )
break;
}
}
SeqPartition¶
- int cvSeqPartition(const CvSeq* seq, CvMemStorage* storage, CvSeq** labels, CvCmpFunc is_equal, void* userdata)¶
Splits a sequence into equivalency classes.
Parameters: - seq – The sequence to partition
- storage – The storage block to store the sequence of equivalency classes. If it is NULL, the function uses seq->storage for output labels
- labels – Ouput parameter. Double pointer to the sequence of 0-based labels of input sequence elements
- is_equal – The relation function that should return non-zero if the two particular sequence elements are from the same class, and zero otherwise. The partitioning algorithm uses transitive closure of the relation function as an equivalency critria
- userdata – Pointer that is transparently passed to the is_equal function
typedef int (CV_CDECL* CvCmpFunc)(const void* a, const void* b, void* userdata);
The function cvSeqPartition implements a quadratic algorithm for splitting a set into one or more equivalancy classes. The function returns the number of equivalency classes.
#include "cxcore.h"
#include "highgui.h"
#include <stdio.h>
CvSeq* point_seq = 0;
IplImage* canvas = 0;
CvScalar* colors = 0;
int pos = 10;
int is_equal( const void* _a, const void* _b, void* userdata )
{
CvPoint a = *(const CvPoint*)_a;
CvPoint b = *(const CvPoint*)_b;
double threshold = *(double*)userdata;
return (double)((a.x - b.x)*(a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y)*(a.y - b.y)) <=
threshold;
}
void on_track( int pos )
{
CvSeq* labels = 0;
double threshold = pos*pos;
int i, class_count = cvSeqPartition( point_seq,
0,
&labels,
is_equal,
&threshold );
printf("
cvZero( canvas );
for( i = 0; i < labels->total; i++ )
{
CvPoint pt = *(CvPoint*)cvGetSeqElem( point_seq, i );
CvScalar color = colors[*(int*)cvGetSeqElem( labels, i )];
cvCircle( canvas, pt, 1, color, -1 );
}
cvShowImage( "points", canvas );
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
CvMemStorage* storage = cvCreateMemStorage(0);
point_seq = cvCreateSeq( CV_32SC2,
sizeof(CvSeq),
sizeof(CvPoint),
storage );
CvRNG rng = cvRNG(0xffffffff);
int width = 500, height = 500;
int i, count = 1000;
canvas = cvCreateImage( cvSize(width,height), 8, 3 );
colors = (CvScalar*)cvAlloc( count*sizeof(colors[0]) );
for( i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
CvPoint pt;
int icolor;
pt.x = cvRandInt( &rng )
pt.y = cvRandInt( &rng )
cvSeqPush( point_seq, &pt );
icolor = cvRandInt( &rng ) | 0x00404040;
colors[i] = CV_RGB(icolor & 255,
(icolor >> 8)&255,
(icolor >> 16)&255);
}
cvNamedWindow( "points", 1 );
cvCreateTrackbar( "threshold", "points", &pos, 50, on_track );
on_track(pos);
cvWaitKey(0);
return 0;
}
Help and Feedback
You did not find what you were looking for?- Ask a question in the user group/mailing list.
- If you think something is missing or wrong in the documentation, please file a bug report.
