Histograms¶
CvHistogram¶
- class CvHistogram¶
Multi-dimensional histogram.
A CvHistogram is a multi-dimensional histogram, created by function CreateHist . It has an attribute bins a CvMatND containing the histogram counts.
CalcBackProject¶
- CalcBackProject(image, back_project, hist) → None¶
Calculates the back projection.
Parameters: - image (sequence of IplImage) – Source images (though you may pass CvMat** as well)
- back_project (CvArr) – Destination back projection image of the same type as the source images
- hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
The function calculates the back project of the histogram. For each tuple of pixels at the same position of all input single-channel images the function puts the value of the histogram bin, corresponding to the tuple in the destination image. In terms of statistics, the value of each output image pixel is the probability of the observed tuple given the distribution (histogram). For example, to find a red object in the picture, one may do the following:
- Calculate a hue histogram for the red object assuming the image contains only this object. The histogram is likely to have a strong maximum, corresponding to red color.
- Calculate back projection of a hue plane of input image where the object is searched, using the histogram. Threshold the image.
- Find connected components in the resulting picture and choose the right component using some additional criteria, for example, the largest connected component.
That is the approximate algorithm of Camshift color object tracker, except for the 3rd step, instead of which CAMSHIFT algorithm is used to locate the object on the back projection given the previous object position.
CalcBackProjectPatch¶
- CalcBackProjectPatch(images, dst, patch_size, hist, method, factor) → None¶
Locates a template within an image by using a histogram comparison.
Parameters: - images (sequence of IplImage) – Source images (though, you may pass CvMat** as well)
- dst (CvArr) – Destination image
- patch_size (CvSize) – Size of the patch slid though the source image
- hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
- method (int) – Comparison method, passed to CompareHist (see description of that function)
- factor (float) – Normalization factor for histograms, will affect the normalization scale of the destination image, pass 1 if unsure
The function calculates the back projection by comparing histograms of the source image patches with the given histogram. Taking measurement results from some image at each location over ROI creates an array image . These results might be one or more of hue, x derivative, y derivative, Laplacian filter, oriented Gabor filter, etc. Each measurement output is collected into its own separate image. The image image array is a collection of these measurement images. A multi-dimensional histogram hist is constructed by sampling from the image image array. The final histogram is normalized. The hist histogram has as many dimensions as the number of elements in image array.
Each new image is measured and then converted into an image image array over a chosen ROI. Histograms are taken from this image image in an area covered by a “patch” with an anchor at center as shown in the picture below. The histogram is normalized using the parameter norm_factor so that it may be compared with hist . The calculated histogram is compared to the model histogram; hist uses The function cvCompareHist with the comparison method= method ). The resulting output is placed at the location corresponding to the patch anchor in the probability image dst . This process is repeated as the patch is slid over the ROI. Iterative histogram update by subtracting trailing pixels covered by the patch and adding newly covered pixels to the histogram can save a lot of operations, though it is not implemented yet.
Back Project Calculation by Patches
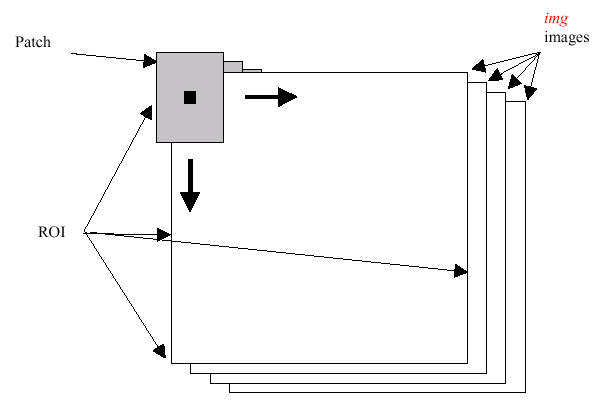
CalcHist¶
- CalcHist(image, hist, accumulate=0, mask=NULL) → None¶
Calculates the histogram of image(s).
Parameters: - image (sequence of IplImage) – Source images (though you may pass CvMat** as well)
- hist (CvHistogram) – Pointer to the histogram
- accumulate (int) – Accumulation flag. If it is set, the histogram is not cleared in the beginning. This feature allows user to compute a single histogram from several images, or to update the histogram online
- mask (CvArr) – The operation mask, determines what pixels of the source images are counted
The function calculates the histogram of one or more single-channel images. The elements of a tuple that is used to increment a histogram bin are taken at the same location from the corresponding input images.
CalcProbDensity¶
- CalcProbDensity(hist1, hist2, dst_hist, scale=255) → None¶
Divides one histogram by another.
Parameters: - hist1 (CvHistogram) – first histogram (the divisor)
- hist2 (CvHistogram) – second histogram
- dst_hist (CvHistogram) – destination histogram
- scale (float) – scale factor for the destination histogram
The function calculates the object probability density from the two histograms as:
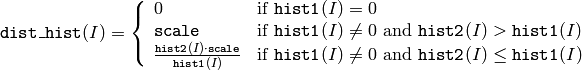
So the destination histogram bins are within less than scale .
ClearHist¶
- ClearHist(hist) → None¶
Clears the histogram.
Parameters: hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
The function sets all of the histogram bins to 0 in the case of a dense histogram and removes all histogram bins in the case of a sparse array.
CompareHist¶
- CompareHist(hist1, hist2, method) → float¶
Compares two dense histograms.
Parameters: - hist1 (CvHistogram) – The first dense histogram
- hist2 (CvHistogram) – The second dense histogram
- method (int) –
Comparison method, one of the following:
- CV_COMP_CORREL Correlation
- CV_COMP_CHISQR Chi-Square
- CV_COMP_INTERSECT Intersection
- CV_COMP_BHATTACHARYYA Bhattacharyya distance
The function compares two dense histograms using the specified method (
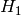 denotes the first histogram,
denotes the first histogram,
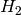 the second):
the second):
Correlation (method=CV_COMP_CORREL)
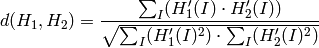
where
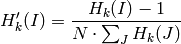
where N is the number of histogram bins.
Chi-Square (method=CV_COMP_CHISQR)
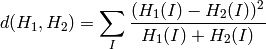
Intersection (method=CV_COMP_INTERSECT)
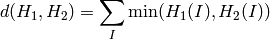
Bhattacharyya distance (method=CV_COMP_BHATTACHARYYA)
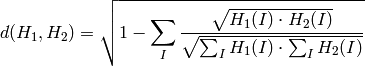
The function returns
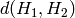 .
.
Note: the method CV_COMP_BHATTACHARYYA only works with normalized histograms.
To compare a sparse histogram or more general sparse configurations of weighted points, consider using the CalcEMD2 function.
CreateHist¶
- CreateHist(dims, type, ranges, uniform = 1) → hist¶
Creates a histogram.
Parameters: - dims (sequence of int) – for an N-dimensional histogram, list of length N giving the size of each dimension
- type (int) – Histogram representation format: CV_HIST_ARRAY means that the histogram data is represented as a multi-dimensional dense array CvMatND; CV_HIST_SPARSE means that histogram data is represented as a multi-dimensional sparse array CvSparseMat
- ranges (list of tuples of ints) – Array of ranges for the histogram bins. Its meaning depends on the uniform parameter value. The ranges are used for when the histogram is calculated or backprojected to determine which histogram bin corresponds to which value/tuple of values from the input image(s)
- uniform (int) – Uniformity flag; if not 0, the histogram has evenly
spaced bins and for every
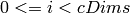 ranges[i]
is an array of two numbers: lower and upper boundaries for the i-th
histogram dimension.
The whole range [lower,upper] is then split
into dims[i] equal parts to determine the i-th input
tuple value ranges for every histogram bin. And if uniform=0 ,
then i-th element of ranges array contains dims[i]+1 elements:
ranges[i]
is an array of two numbers: lower and upper boundaries for the i-th
histogram dimension.
The whole range [lower,upper] is then split
into dims[i] equal parts to determine the i-th input
tuple value ranges for every histogram bin. And if uniform=0 ,
then i-th element of ranges array contains dims[i]+1 elements: ![\texttt{lower}_0, \texttt{upper}_0,
\texttt{lower}_1, \texttt{upper}_1 = \texttt{lower}_2,
...
\texttt{upper}_{dims[i]-1}](_images/math/fe08982429265eddcede7828aedeabdefc8315dd.png) where
where  and
and 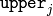 are lower and upper
boundaries of i-th input tuple value for j-th
bin, respectively. In either case, the input values that are beyond
the specified range for a histogram bin are not counted by CalcHist and filled with 0 by CalcBackProject
are lower and upper
boundaries of i-th input tuple value for j-th
bin, respectively. In either case, the input values that are beyond
the specified range for a histogram bin are not counted by CalcHist and filled with 0 by CalcBackProject
The function creates a histogram of the specified size and returns a pointer to the created histogram. If the array ranges is 0, the histogram bin ranges must be specified later via the function SetHistBinRanges . Though CalcHist and CalcBackProject may process 8-bit images without setting bin ranges, they assume thy are equally spaced in 0 to 255 bins.
GetMinMaxHistValue¶
- GetMinMaxHistValue(hist)-> (min_value, max_value, min_idx, max_idx)¶
Finds the minimum and maximum histogram bins.
Parameters: - hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
- min_value (CvScalar) – Minimum value of the histogram
- max_value (CvScalar) – Maximum value of the histogram
- min_idx (sequence of int) – Coordinates of the minimum
- max_idx (sequence of int) – Coordinates of the maximum
The function finds the minimum and maximum histogram bins and their positions. All of output arguments are optional. Among several extremas with the same value the ones with the minimum index (in lexicographical order) are returned. In the case of several maximums or minimums, the earliest in lexicographical order (extrema locations) is returned.
NormalizeHist¶
- NormalizeHist(hist, factor) → None¶
Normalizes the histogram.
Parameters: - hist (CvHistogram) – Pointer to the histogram
- factor (float) – Normalization factor
The function normalizes the histogram bins by scaling them, such that the sum of the bins becomes equal to factor .
QueryHistValue_1D¶
- QueryHistValue_1D(hist, idx0) → float¶
Returns the value from a 1D histogram bin.
Parameters: - hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
- idx0 (int) – bin index 0
QueryHistValue_2D¶
- QueryHistValue_2D(hist, idx0, idx1) → float¶
Returns the value from a 2D histogram bin.
Parameters: - hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
- idx0 (int) – bin index 0
- idx1 (int) – bin index 1
QueryHistValue_3D¶
- QueryHistValue_3D(hist, idx0, idx1, idx2) → float¶
Returns the value from a 3D histogram bin.
Parameters: - hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
- idx0 (int) – bin index 0
- idx1 (int) – bin index 1
- idx2 (int) – bin index 2
QueryHistValue_nD¶
- QueryHistValue_nD(hist, idx) → float¶
Returns the value from a 1D histogram bin.
Parameters: - hist (CvHistogram) – Histogram
- idx (sequence of int) – list of indices, of same length as the dimension of the histogram’s bin.
ThreshHist¶
- ThreshHist(hist, threshold) → None¶
Thresholds the histogram.
Parameters: - hist (CvHistogram) – Pointer to the histogram
- threshold (float) – Threshold level
The function clears histogram bins that are below the specified threshold.
Help and Feedback
You did not find what you were looking for?- Try the Cookbook.
- Ask a question in the user group/mailing list.
- If you think something is missing or wrong in the documentation, please file a bug report.
