Planar Subdivisions¶
CvSubdiv2D¶
- class CvSubdiv2D¶
Planar subdivision.
Planar subdivision is the subdivision of a plane into a set of non-overlapped regions (facets) that cover the whole plane. The above structure describes a subdivision built on a 2d point set, where the points are linked together and form a planar graph, which, together with a few edges connecting the exterior subdivision points (namely, convex hull points) with infinity, subdivides a plane into facets by its edges.
For every subdivision there exists a dual subdivision in which facets and points (subdivision vertices) swap their roles, that is, a facet is treated as a vertex (called a virtual point below) of the dual subdivision and the original subdivision vertices become facets. On the picture below original subdivision is marked with solid lines and dual subdivision with dotted lines.
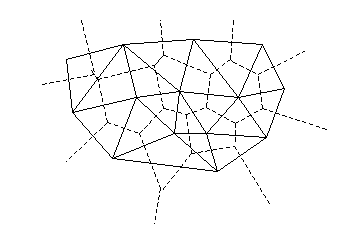
OpenCV subdivides a plane into triangles using Delaunay’s algorithm. Subdivision is built iteratively starting from a dummy triangle that includes all the subdivision points for sure. In this case the dual subdivision is a Voronoi diagram of the input 2d point set. The subdivisions can be used for the 3d piece-wise transformation of a plane, morphing, fast location of points on the plane, building special graphs (such as NNG,RNG) and so forth.
CvSubdiv2DPoint¶
- class CvSubdiv2DPoint¶
Point of original or dual subdivision.
- first¶
A connected CvSubdiv2DEdge
- pt¶
Position, as a CvPoint2D32f
CalcSubdivVoronoi2D¶
- CalcSubdivVoronoi2D(subdiv) → None¶
Calculates the coordinates of Voronoi diagram cells.
Parameters: subdiv (CvSubdiv2D) – Delaunay subdivision, in which all the points are already added
The function calculates the coordinates of virtual points. All virtual points corresponding to some vertex of the original subdivision form (when connected together) a boundary of the Voronoi cell at that point.
ClearSubdivVoronoi2D¶
- ClearSubdivVoronoi2D(subdiv) → None¶
Removes all virtual points.
Parameters: subdiv (CvSubdiv2D) – Delaunay subdivision
The function removes all of the virtual points. It is called internally in CalcSubdivVoronoi2D if the subdivision was modified after previous call to the function.
CreateSubdivDelaunay2D¶
- CreateSubdivDelaunay2D(rect, storage) → delaunay_triangulation¶
Creates an empty Delaunay triangulation.
Parameters: - rect (CvRect) – Rectangle that includes all of the 2d points that are to be added to the subdivision
- storage (CvMemStorage) – Container for subdivision
The function creates an empty Delaunay subdivision, where 2d points can be added using the function SubdivDelaunay2DInsert . All of the points to be added must be within the specified rectangle, otherwise a runtime error will be raised.
Note that the triangulation is a single large triangle that covers the given rectangle. Hence the three vertices of this triangle are outside the rectangle rect .
FindNearestPoint2D¶
- FindNearestPoint2D(subdiv, pt) → point¶
Finds the closest subdivision vertex to the given point.
Parameters: - subdiv (CvSubdiv2D) – Delaunay or another subdivision
- pt (CvPoint2D32f) – Input point
The function is another function that locates the input point within the subdivision. It finds the subdivision vertex that is the closest to the input point. It is not necessarily one of vertices of the facet containing the input point, though the facet (located using Subdiv2DLocate ) is used as a starting point. The function returns a pointer to the found subdivision vertex.
Subdiv2DEdgeDst¶
- Subdiv2DEdgeDst(edge) → point¶
Returns the edge destination.
Parameters: edge (CvSubdiv2DEdge) – Subdivision edge (not a quad-edge)
The function returns the edge destination. The returned pointer may be NULL if the edge is from dual subdivision and the virtual point coordinates are not calculated yet. The virtual points can be calculated using the function CalcSubdivVoronoi2D .
Subdiv2DGetEdge¶
- Subdiv2DGetEdge(edge, type) → CvSubdiv2DEdge¶
Returns one of the edges related to the given edge.
Parameters: - edge (CvSubdiv2DEdge) – Subdivision edge (not a quad-edge)
- type – Specifies which of the related edges to return, one of the following:
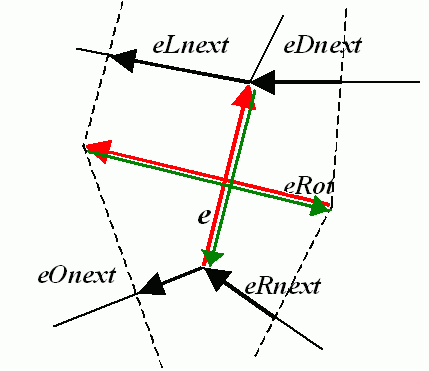
The function returns one of the edges related to the input edge.
Subdiv2DNextEdge¶
- Subdiv2DNextEdge(edge) → CvSubdiv2DEdge¶
Returns next edge around the edge origin
Parameters: edge (CvSubdiv2DEdge) – Subdivision edge (not a quad-edge)

The function returns the next edge around the edge origin: eOnext on the picture above if e is the input edge)
Subdiv2DLocate¶
- Subdiv2DLocate(subdiv, pt) -> (loc, where)¶
Returns the location of a point within a Delaunay triangulation.
Parameters: - subdiv (CvSubdiv2D) – Delaunay or another subdivision
- pt (CvPoint2D32f) – The point to locate
- loc (int) – The location of the point within the triangulation
- where (CvSubdiv2DEdge, CvSubdiv2DPoint) – The edge or vertex. See below.
The function locates the input point within the subdivision. There are 5 cases:
- The point falls into some facet. loc is CV_PTLOC_INSIDE and where is one of edges of the facet.
- The point falls onto the edge. loc is CV_PTLOC_ON_EDGE and where is the edge.
- The point coincides with one of the subdivision vertices. loc is CV_PTLOC_VERTEX and where is the vertex.
- The point is outside the subdivsion reference rectangle. loc is CV_PTLOC_OUTSIDE_RECT and where is None.
- One of input arguments is invalid. The function raises an exception.
Subdiv2DRotateEdge¶
- Subdiv2DRotateEdge(edge, rotate) → CvSubdiv2DEdge¶
Returns another edge of the same quad-edge.
Parameters: - edge (CvSubdiv2DEdge) – Subdivision edge (not a quad-edge)
- rotate (int) –
Specifies which of the edges of the same quad-edge as the input one to return, one of the following:
- 0 the input edge ( e on the picture below if e is the input edge)
- 1 the rotated edge ( eRot )
- 2 the reversed edge (reversed e (in green))
- 3 the reversed rotated edge (reversed eRot (in green))

The function returns one of the edges of the same quad-edge as the input edge.
SubdivDelaunay2DInsert¶
- SubdivDelaunay2DInsert(subdiv, pt) → point¶
Inserts a single point into a Delaunay triangulation.
Parameters: - subdiv (CvSubdiv2D) – Delaunay subdivision created by the function CreateSubdivDelaunay2D
- pt (CvPoint2D32f) – Inserted point
The function inserts a single point into a subdivision and modifies the subdivision topology appropriately. If a point with the same coordinates exists already, no new point is added. The function returns a pointer to the allocated point. No virtual point coordinates are calculated at this stage.
Help and Feedback
You did not find what you were looking for?- Try the Cookbook.
- Ask a question in the user group/mailing list.
- If you think something is missing or wrong in the documentation, please file a bug report.
