Non-local Means Filterによるデノイジング
Non-local means
filterと呼ばれるフィルタによるノイズ除去処理のデモンストレーションです.このデモは下記論文の実装です.詳細はそちらで確認して下さい.テクスチャ(模様)の多い画像などで,特に効果を発揮し,バイラテラルフィルタよりも効果の高いフィルタとなります.
A. Buades, B. Coll, J.M. Morel “A non local algorithm for image denoising”
IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2005, Vol 2, pp: 60-65, 2005.
下のデモンストレーションビデオでは,画像にガウシアンノイズを付加し,様々な手法とこのNon-local means
filterでのノイズ除去をデモンストレーションしています.
質問等やバグ報告は@fukushima1981(Twitter)までどうぞ.
※ 下記質問に対するバグ修正(とコードの最適化)を行っております.(2011/11/23)
C++
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// additional functions/////////////////////////////////////
void addNoiseSoltPepperMono(Mat& src, Mat& dest,double per)
{
cv::RNG rng;
#pragma omp parallel for
for(int j=0;j<src.rows;j++)
{
uchar* s=src.ptr(j);
uchar* d=dest.ptr(j);
for(int i=0;i<src.cols;i++)
{
double a1 = rng.uniform((double)0, (double)1);
if(a1>per)
d[i]=s[i];
else
{
double a2 = rng.uniform((double)0, (double)1);
if(a2>0.5)d[i]=0;
else d[i]=255;
}
}
}
}
void addNoiseMono(Mat& src, Mat& dest,double sigma)
{
Mat s;
src.convertTo(s,CV_16S);
Mat n(s.size(),CV_16S);
randn(n,0,sigma);
Mat temp = s+n;
temp.convertTo(dest,CV_8U);
}
void addNoise(Mat&src, Mat& dest, double sigma,double sprate=0.0)
{
if(src.channels()==1)
{
addNoiseMono(src,dest,sigma);
if(sprate!=0)addNoiseSoltPepperMono(dest,dest,sprate);
return;
}
else
{
vector<Mat> s;
vector<Mat> d(src.channels());
split(src,s);
for(int i=0;i<src.channels();i++)
{
addNoiseMono(s[i],d[i],sigma);
if(sprate!=0)addNoiseSoltPepperMono(d[i],d[i],sprate);
}
cv::merge(d,dest);
}
}
static double getPSNR(Mat& src, Mat& dest)
{
int i,j;
double sse,mse,psnr;
sse = 0.0;
for(j=0;j<src.rows;j++)
{
uchar* d=dest.ptr(j);
uchar* s=src.ptr(j);
for(i=0;i<src.cols;i++)
{
sse += ((d[i] - s[i])*(d[i] - s[i]));
}
}
if(sse == 0.0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
mse =sse /(double)(src.cols*src.rows);
psnr = 10.0*log10((255*255)/mse);
return psnr;
}
}
double calcPSNR(Mat& src, Mat& dest)
{
Mat ssrc;
Mat ddest;
if(src.channels()==1)
{
src.copyTo(ssrc);
dest.copyTo(ddest);
}
else
{
cvtColor(src,ssrc,CV_BGR2YUV);
cvtColor(dest,ddest,CV_BGR2YUV);
}
double sn = getPSNR(ssrc,ddest);
return sn;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//main implementaion
void nonlocalMeansFilter(Mat& src, Mat& dest, int templeteWindowSize, int searchWindowSize, double h, double sigma=0.0)
{
if(templeteWindowSize>searchWindowSize)
{
cout<<"searchWindowSize should be larger than templeteWindowSize"<<endl;
return;
}
if(dest.empty())dest=Mat::zeros(src.size(),src.type());
const int tr = templeteWindowSize>>1;
const int sr = searchWindowSize>>1;
const int bb = sr+tr;
const int D = searchWindowSize*searchWindowSize;
const int H=D/2+1;
const double div = 1.0/(double)D;//search area div
const int tD = templeteWindowSize*templeteWindowSize;
const double tdiv = 1.0/(double)(tD);//templete square div
//create large size image for bounding box;
Mat im;
copyMakeBorder(src,im,bb,bb,bb,bb,cv::BORDER_DEFAULT);
//weight computation;
vector<double> weight(256*256*src.channels());
double* w = &weight[0];
const double gauss_sd = (sigma == 0.0) ? h :sigma;
double gauss_color_coeff = -(1.0/(double)(src.channels()))*(1.0/(h*h));
int emax;
for(int i = 0; i < 256*256*src.channels(); i++ )
{
double v = std::exp( max(i-2.0*gauss_sd*gauss_sd,0.0)*gauss_color_coeff);
w[i] = v;
if(v<0.001)
{
emax=i;
break;
}
}
for(int i = emax; i < 256*256*src.channels(); i++ )w[i] = 0.0;
if(src.channels()==3)
{
const int cstep = im.step-templeteWindowSize*3;
const int csstep = im.step-searchWindowSize*3;
#pragma omp parallel for
for(int j=0;j<src.rows;j++)
{
uchar* d = dest.ptr(j);
int* ww=new int[D];
double* nw=new double[D];
for(int i=0;i<src.cols;i++)
{
double tweight=0.0;
//search loop
uchar* tprt = im.data +im.step*(sr+j) + 3*(sr+i);
uchar* sptr2 = im.data +im.step*j + 3*i;
for(int l=searchWindowSize,count=D-1;l--;)
{
uchar* sptr = sptr2 +im.step*(l);
for (int k=searchWindowSize;k--;)
{
//templete loop
int e=0;
uchar* t = tprt;
uchar* s = sptr+3*k;
for(int n=templeteWindowSize;n--;)
{
for(int m=templeteWindowSize;m--;)
{
// computing color L2 norm
e += (s[0]-t[0])*(s[0]-t[0])+(s[1]-t[1])*(s[1]-t[1])+(s[2]-t[2])*(s[2]-t[2]);//L2 norm
s+=3,t+=3;
}
t+=cstep;
s+=cstep;
}
const int ediv = e*tdiv;
ww[count--]=ediv;
//get weighted Euclidean distance
tweight+=w[ediv];
}
}
//weight normalization
if(tweight==0.0)
{
for(int z=0;z<D;z++) nw[z]=0;
nw[H]=1;
}
else
{
double itweight=1.0/(double)tweight;
for(int z=0;z<D;z++) nw[z]=w[ww[z]]*itweight;
}
double r=0.0,g=0.0,b=0.0;
uchar* s = im.ptr(j+tr); s+=3*(tr+i);
for(int l=searchWindowSize,count=0;l--;)
{
for(int k=searchWindowSize;k--;)
{
r += s[0]*nw[count];
g += s[1]*nw[count];
b += s[2]*nw[count++];
s+=3;
}
s+=csstep;
}
d[0] = saturate_cast<uchar>(r);
d[1] = saturate_cast<uchar>(g);
d[2] = saturate_cast<uchar>(b);
d+=3;
}//i
delete[] ww;
delete[] nw;
}//j
}
else if(src.channels()==1)
{
const int cstep = im.step-templeteWindowSize;
const int csstep = im.step-searchWindowSize;
#pragma omp parallel for
for(int j=0;j<src.rows;j++)
{
uchar* d = dest.ptr(j);
int* ww=new int[D];
double* nw=new double[D];
for(int i=0;i<src.cols;i++)
{
double tweight=0.0;
//search loop
uchar* tprt = im.data +im.step*(sr+j) + (sr+i);
uchar* sptr2 = im.data +im.step*j + i;
for(int l=searchWindowSize,count=D-1;l--;)
{
uchar* sptr = sptr2 +im.step*(l);
for (int k=searchWindowSize;k--;)
{
//templete loop
int e=0;
uchar* t = tprt;
uchar* s = sptr+k;
for(int n=templeteWindowSize;n--;)
{
for(int m=templeteWindowSize;m--;)
{
// computing color L2 norm
e += (*s-*t)*(*s-*t);
s++,t++;
}
t+=cstep;
s+=cstep;
}
const int ediv = e*tdiv;
ww[count--]=ediv;
//get weighted Euclidean distance
tweight+=w[ediv];
}
}
//weight normalization
if(tweight==0.0)
{
for(int z=0;z<D;z++) nw[z]=0;
nw[H]=1;
}
else
{
double itweight=1.0/(double)tweight;
for(int z=0;z<D;z++) nw[z]=w[ww[z]]*itweight;
}
double v=0.0;
uchar* s = im.ptr(j+tr); s+=(tr+i);
for(int l=searchWindowSize,count=0;l--;)
{
for(int k=searchWindowSize;k--;)
{
v += *(s++)*nw[count++];
}
s+=csstep;
}
*(d++) = saturate_cast<uchar>(v);
}//i
delete[] ww;
delete[] nw;
}//j
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
//(1) Reading image and add noise(standart deviation = 15)
const double noise_sigma = 15.0;
Mat src = imread("lenna.png",1);
Mat snoise;
Mat dest;
addNoise(src,snoise,noise_sigma);
//(2) preview conventional method with PSNR
//(2-1) RAW
cout<<"RAW: "<<calcPSNR(src,snoise)<<endl<<endl;
imwrite("noise.png",snoise);
//(2-2) Gaussian Filter (7x7) sigma = 5
int64 pre = getTickCount();
GaussianBlur(snoise,dest,Size(7,7),5);
cout<<"time: "<<1000.0*(getTickCount()-pre)/(getTickFrequency())<<" ms"<<endl;
cout<<"gaussian: "<<calcPSNR(src,dest)<<endl<<endl;
imwrite("gaussian.png",dest);
//(2-3) median Filter (3x3)
pre = getTickCount();
medianBlur(snoise,dest,3);
cout<<"time: "<<1000.0*(getTickCount()-pre)/(getTickFrequency())<<" ms"<<endl;
cout<<"median: "<<calcPSNR(src,dest)<<endl<<endl;
imwrite("median.png",dest);
//(2-4) Bilateral Filter (7x7) color sigma = 35, space sigma = 5
pre = getTickCount();
bilateralFilter(snoise,dest,7,35,5);
cout<<"time: "<<1000.0*(getTickCount()-pre)/(getTickFrequency())<<" ms"<<endl;
cout<<"bilateral: "<<calcPSNR(src,dest)<<endl<<endl;
imwrite("bilateral.png",dest);
//(3) analizing of performance of Nonlocal means filter
pre = getTickCount();
nonlocalMeansFilter(snoise,dest,3,7,noise_sigma,noise_sigma);
cout<<"time: "<<1000.0*(getTickCount()-pre)/(getTickFrequency())<<" ms"<<endl;
cout<<"nonlocal: "<<calcPSNR(src,dest)<<endl<<endl;
imwrite("nonlocal.png",dest);
imshow("noise", snoise);
imshow("Non-local Means Filter", dest);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
(1)画像の読み込みとノイズの付加
画像を読み込み,標準偏差15のガウシアンノイズを付加します.
(2)比較手法の画像品質をPSNRで評価
下記手法で,ノイズ除去をしたのちに,原画像と比較することでPSNRを求めます.
(2-1)フィルタなし(処理無し)
(2-2)ガウシアンフィルタ(7x7),標準偏差5
(2-3)メディアンフィルタ(3x3)
(2-4)バイラテラルフィルタ(7x7),色標準偏差35,位置標準偏差5
(3)Non-local means filterの概説
Non-local means
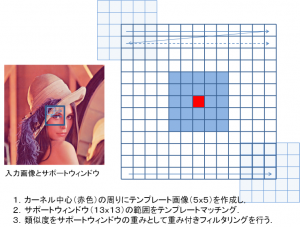
filterとは,適応的な重みを持つサポートウィンドウのコンボルージョンによりノイズリダクションするフィルタで,エッジキープ型のフィルタとなります.その重みは,カーネル中心まわりにサポートよりも小さなテンプレートを作成し,テンプレートマッチングによりサポートウィンドウ内の類似度(重み付きユークリッド距離,L2ノルムのエクスポネンシャル)を各位置ごとに求めていきます.その類似度により,テンプレートに似ている位置の重みを大きく,似ていない位置の重みは小さく設定されます.図に概略を示します.
また,類似したフィルタには,バイラテラルフィルタがあり,Non-local means
filterのテンプレートサイズが(1×1)の時,位置重みの無いバイラテラルフィルタとなります.
数式等の詳細を図式注釈に埋め込みました.詳細が知りたい方はそこを参照してください.
(4)結果およびまとめ
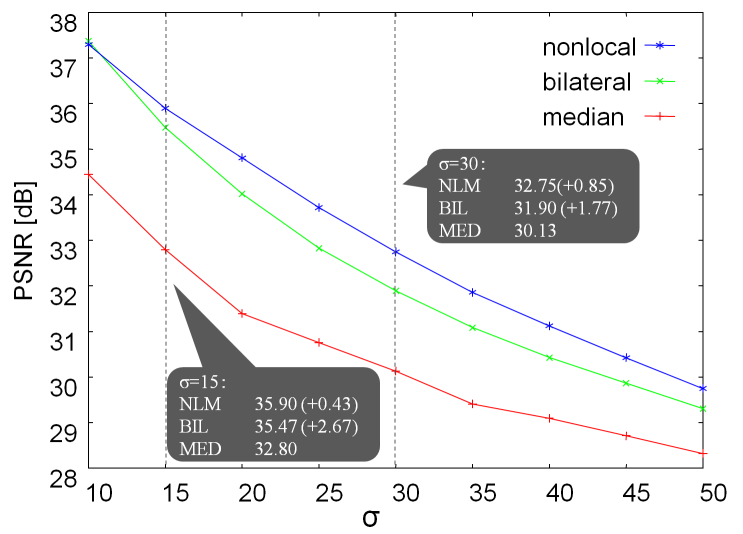
画質評価の指標であるPSNRを計測すると,フィルタなし 28.0 dB,ガウシアン 30.5 dB,メディアン 32.8 dB,バイラテラル 33.6 dB,ノンローカル 35.3
dB となりました.
大きな画質改善がみられるメディアン,バイラテラル,ノンローカルの各手法で,強さを変えての画像にノイズを付加した画像をノイズ除去を行った結果が下記グラフです.

ノンローカルは最もノイズ除去効果が高く,特にノイズが大きいときにバイラテラルより効果的なことがわかります.図に示す画像からも効果がよくわかります.
また計算時間は,
メディアン 0.8ms,
ガウシアン 3.5ms,
バイラテラル 103ms,
ノンローカル 524ms(並列化なし),128ms(並列化あり)(※バグ修正&コード最適化前は並列化なしで684ms)
となり,このフィルタの計算時間が非常に大きいことがわかります.しかしこれは安直な実装であり,下記論文などのいくつかの高速化手法も提案されています.なお,実験環境はCore i7 2.93GHzで行いました.
J. Wang, Y. Guo, Y. Ying, Y. Liu, Q. Peng, “Fast Non-Local Algorithm for Image Denoising,” in Proc. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2006 (ICIP2006), pp. 1429 – 1432, Oct. 2006.
下記画像は左上段(入力画像),右上段(ノイズ付加画像),左中段(ガウシアンフィルタ),右中段(メディアンフィルタ),左下段(バイラテラルフィルタ),右下段(Non-local means Filter)となっています.